
Today, most of the world's primary energy comes from fuels, mostly fossil fuels. These fuels are dangerous for the planet because they release carbon dioxide during combustion. Despite this, the world's primary energy supply is growing at a faster rate than the world's population, especially in fast-growing economies like the BRIC countries.
Renewable energy sources
Renewable energy sources are energy resources that can be continuously replenished and are renewable. Renewable energy sources are energy sources that can be created at any moment. While fossil fuels can take millions of year to form, they can be made instantly. These resources are a great source to heat and electricity. These energy sources, however, can only be used in specific conditions. Storage solutions are needed to ensure that there is a constant and reliable supply.
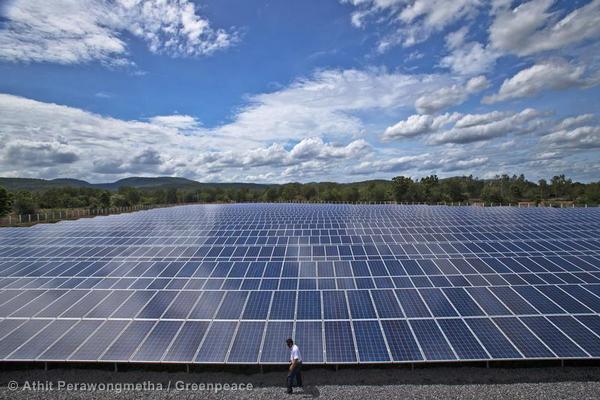
Renewable energy has widespread support. Both solar and wind energy can produce electricity with no carbon emissions. Depending on the technology, they might be economical to use for large-scale projects. Solar and wind power are not reliable, so a backup generator is necessary. This means that you will pay more to power an entire network if you are using these resources.
Coal
Coal has been used in energy production for thousands years. It was used for heating public baths during the Roman Empire, Aztec Empire, as well as the Industrial Revolution. Because of its high energy content, it was an attractive alternative to wood fuel. It produces steam which is used to power steamships. Northern England was home to coal, which was then mined at over 80% in the early 18th-century.

Coal poses a significant health risk. According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer, coal can cause lung cancer. IARC lists many pollutants that are associated with coal production and combustion as human carcinogens. These pollutants can also cause outdoor air pollution such as radon. Improved air quality is associated with improved health, as coal has been linked to lung cancer. Many countries have enacted legislation to reduce air pollution.
Natural gas
History of energy has seen a gradual transition from cheap, polluted fuels to cleaner, more efficient ones. Machines and mills replaced manual labor, coal and oil replaced wood for heating buildings and industry, and electricity replaced kerosene and whale oil. Natural gas has become a cleaner, cheaper option.
Natural gas is a gas that naturally occurs underground. It can often be found in the same place as oil, making it easy and convenient to find. In the beginning days of the oil business, gas was often wasted. However, natural gases are now highly valued for their clean combustion and use in industrial processes. Access to this resource is not possible without the right infrastructure.
Wind
Wind is one among the fastest-growing energy sources around the globe. It has inherent challenges in some regions, but is also incredibly affordable in many. Wind power is competitive with other forms, in certain regions. R&D efforts worldwide are focused on lowering the levelized cost for electricity produced by wind.
Wind turbines generate wind energy using the kinetic energy of wind. To harness the wind's power, the turbine's blades turn in a clockwise motion. This wind energy travels through the turbine's nacelle and is then converted to electricity. The turbine then converts the wind power into electricity.
Water
Earth has plenty of resources for primary and renewable energy such as water. But our use of these resources depletes them over time. This is especially true for water as the availability of water varies from one place to another. Evaporation is another way that water resources are depleted. The United States consumes approximately 58 trillion gallons per year of freshwater to meet its energy needs.
You can separate energy sources into primary and secondary sources. Primary energy sources are natural resources that can be used to make energy in other forms. You can use water to make electricity or hydrogen. Water is also used to produce heat.